GraphGL
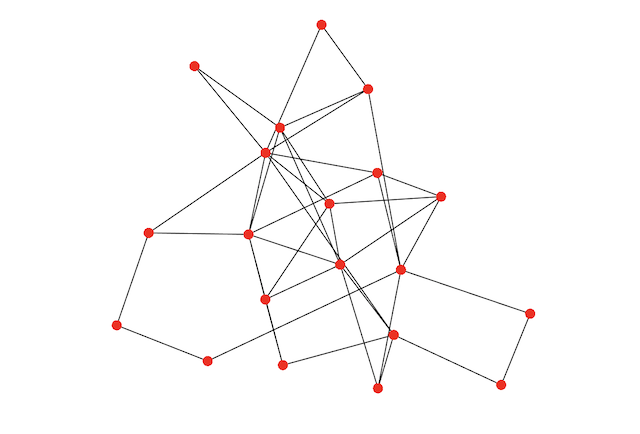
Usage
import GraphGL, {
JSONLoader,
NODE_TYPE,
D3ForceLayout
} from 'graph.gl';
const App = ({data}) => {
const graph = JSONLoader({
json: data,
nodeParser: node => ({id: node.id}),
edgeParser: edge => ({
id: edge.id,
sourceId: edge.sourceId,
targetId: edge.targetId,
directed: true,
}),
});
return (
<GraphGL
graph={graph}
layout={new D3ForceLayout()}
nodeStyle={[
{
type: NODE_TYPE.CIRCLE,
radius: 10,
fill: 'blue',
opacity: 1,
},
]}
edgeStyle={{
stroke: 'black',
strokeWidth: 2,
}}
enableDragging
/>
);
}graph (Graph, required)
The graph data will need to be processed through JSONLoader and converted into Graph object. The expected data should be an object includes two arrays: nodes and edges. Each node require an unique id. Each edge should have id as edge ID, sourceId as the ID of the source node, and targetId as the ID of the target node. For example:
const data = {
nodes: [
{id: '1'}, {id: '2'}, {id: '3'},
],
edges: [
{id: 'e1', sourceId: '1', targetId: '2'},
{id: 'e2', sourceId: '1', targetId: '3'},
{id: 'e3', sourceId: '2', targetId: '3'},
],
};Then, you can convert the data into Graph by JSONLoader:
import {JSONLoader} from 'graph.gl';
const graph = JSONLoader({json: data});layout (Layout, required)
Use one of the layouts provided by Graph.gl or create a new custom layout class by following the instruction. For more detail, please see the Layout section.
initialViewState (Object, optional)
For more detail, please see here.
nodeStyle (Array, required)
A node is made of a set of layers. nodeStyle is a set of style objects to describe the style for each layer. For more detail, please see the explanation of nodeStyle at here.
nodeEvents (Object, optional)
For more detail, please see here.
edgeStyle (Object, required)
For more detail, please see the explanation of edgeStyle at here
edgeEvents (Object, optional)
For more detail, please see here.